How can heat pumps lower my energy bills?
Heat pumps are today considered an environmentally friendlier alternative to traditional fossil fuel heating solutions, such as gas boilers, as they use electricity to generate heat
But why should your business switch to a heat pump – and can you make it even more efficient for your business?
What is a heat pump?
There are typically two types of heat pumps operating effectively in the UK:
Ground Source Heat Pumps that transfer heat from pipes laid underground absorbing the earth’s core temperature, whereas Air Source Heat Pumps use similar technology to products like refrigerators and air-conditioners. They extract heat from the surrounding air (or pipes), which is then amplified and transferred to where the heat is required.
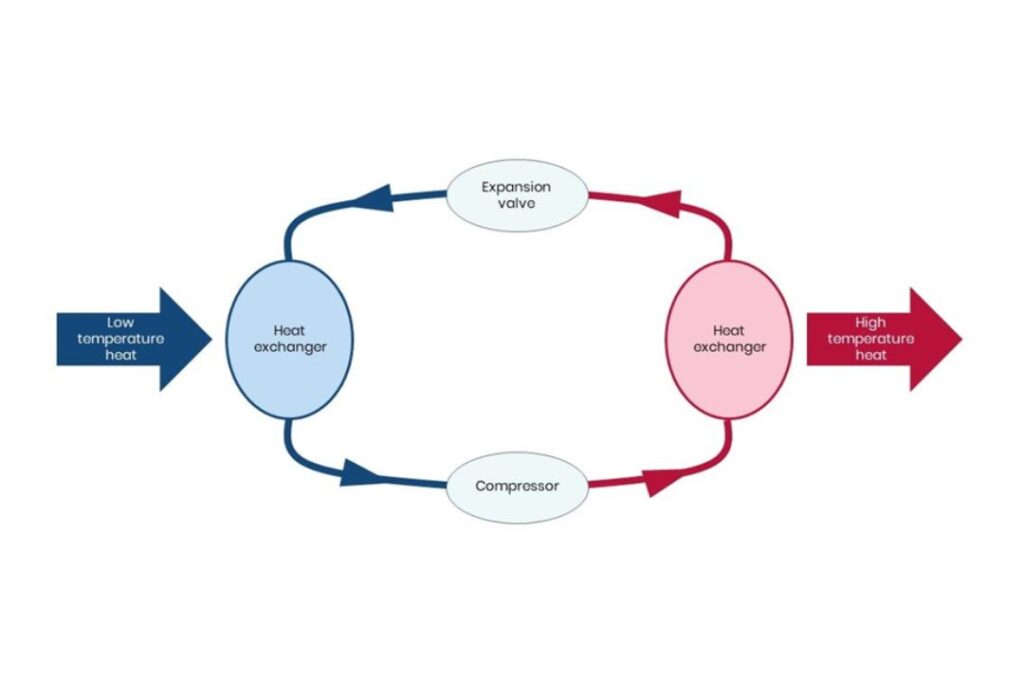
The heat pump output is created by passing the ambient incoming temperature across a plate heat exchanger. On the other side of the exchanger is a filled circuit with normally a refrigerant gas, The gas is then compressed which in turn increases its temperature. As it is transferred on to another heat exchanger, it heats the ‘wet’ heating circuit on the other side which is transferred out via space emitters (radiators) or underfloor heating.
The amount of heat produced for every unit of electricity used is known as the Coefficient of Performance (CoP). So, if a heat pump has a CoP of 3.0, then it will give out three units of heat for every unit of electricity consumed. making it more efficient than current conventional heating technologies such as boilers.
The typical output of thermal heat from a heat pump for space heating is two times more energy-efficient than gas boilers –
However, this is subjective as a heat pump will typically only generate low temperature thermal heat for space heating only, and therefore require additional electricity via immersion heaters to get above 65 degrees, which adds more electrical running costs, whereas a gas boiler will produce & deliver high temp space heating and domestic hot water above 65 degrees as a default operation
Source Energy Saving Trust explanation & diagram below
Integrating your heat pump with a CHP
Heat pumps have a place within commercial applications but are costly to run.
To get the very best out of heat pumps, your business can reinforce their effectiveness with complementary technologies such as a Combined Heat and Power (CHP) unit. Partnering these two technologies can combat the biggest disadvantages associated with heat pumps, high energy costs to run.
Heat transferred using a heat pump will cost your business around 10p/kWh – with grid power costing 30p/kWh with the SCOP for heat pumps at 3:1.
With the addition of a CHP this cost drops to 2.5p/kWh.
Save 75% of your heating costs when partnering a heat pump with a CHP unit.
By producing on-site energy, you can guarantee cheaper rates for electricity than what’s supplied to you via the grid. CHPs also enable heat pumps to retain their impressive efficiency all year round by utilising the higher-grade heat from the CHP to ensure your domestic water heater supply stays above 65 oC instead of using costly immersion heaters.

Achieve your Net Zero targets
Onsite combined heat & power generation provides you with a more sustainable way to power and heat your business facilities. Integrating a CHP engine alongside a heat pump ensures a continued heat and electricity supply, from a source with lower CO2 emissions, with significantly reduced per Kilowatt-Hour cost.
Advantages of heat pumps
1. Save costs on fossil fuels
If your business is currently being heated by fossil fuels such as oil or gas, then replacing this with a heat pump will mean you no longer need to order these fuels to heat your facility. This allows you to heat your business more sustainably, lowering your Scope 2 emissions whilst enjoying a lower monthly gas, or oil bill.
2. Sustainable heating
An Air Source Heat Pump uses only electricity to power and transfer heat around your business facility. With more and more electricity generation options available to UK business owners, options such as on-site generation via a CHP unit, make heat pumps are a great choice when looking to achieve Net Zero targets.
Disadvantages of heat pumps
1. Increased electricity usage
Heat pumps are powered by electricity, which means after installation you are likely to see an increase in electricity usage for your business. This problem is exacerbated if you are currently getting power from the grid, making it hard to budget and track the ROI of your investment as energy costs rarely stay consistent.
2. Diminishing returns
As temperatures drop, the efficiency of heat pumps starts to decline, requiring more power to heat your business. In fact, when temperatures fall below -5 oC, the efficiency of your heat pumps can drop to half in Coefficient of Performance (CoP).
3. Integrated systems
To get more out of your heat pumps, you need to integrate them with other systems, such as immersion heaters, to heat domestic water to safe levels above 65 oC once every 24 hours.
Helec work with you
Helec has been helping business owners get cheaper, cleaner, and more renewable energy for over 17 years. We provide an extensive range of heating and ventilation systems, specialising in only high-efficiency products that exceed today’s standards.
Enable your business to hit the sustainability goals you’re after with the solutions you already have in place by getting in touch.
